Machine learning is no longer an idea limited to investigators or tech hulks. It’s everywhere, from the references you see on Netflix to the voice assistants on your phone. At its essence, machine learning uses data and procedures to make forecasts, learn patterns, and advance presentation over time without being fully automatic.
Why Machine Learning Matters Today
We live in a data-driven biosphere. Businesses, governments, and even individual devices produce massive quantities of data daily. Traditional programming can’t grip this level of difficulty, but machine learning procedures can. They help us make sense of the chaos, leading to keener decisions, automation, and novelties in industries like healthcare, finance, ecommerce, Freelancer Carrers and conveyance.
What Are Machine Learning Algorithms?
A machine learning algorithm is a set of rules or steps a computer follows to know patterns, classify data, or predict consequences. Think of it like educating a child: you deliver examples (data), they learn from those instances, and then they can apply that information to new circumstances.
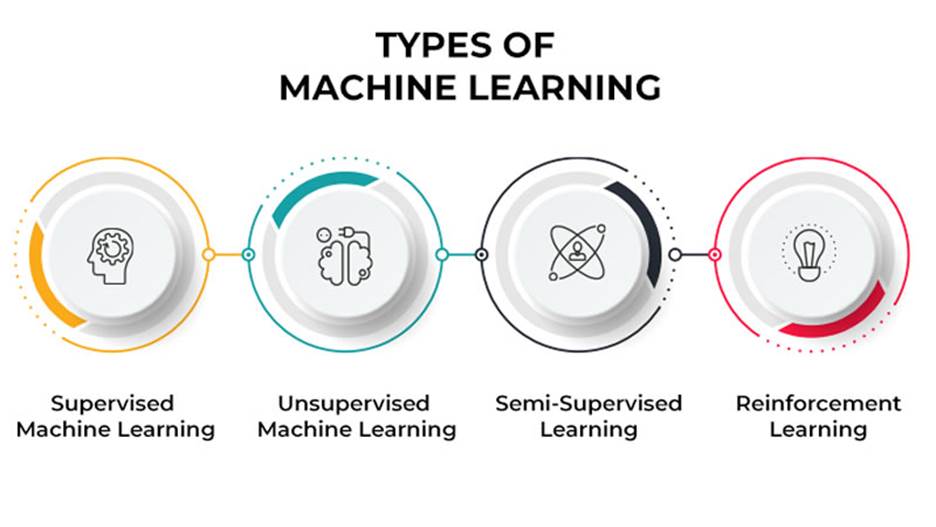
Types of Machine Learning
There are three main types of machine learning algorithms:
Supervised Learning
Here, the algorithm studies from labeled data. Envisage giving a student a math problem with the solution provided over time, and they comprehend how to solve new glitches on their own. Oversaw knowledge is used for organization (like spam detection) and regression (predicting house prices).
Unsupervised Learning
In this type, the data isn’t branded. The algorithm discovers hidden constructions or patterns. For instance, an e-commerce website grouping clients based on buying conduct without prior information about their favorites.
Reinforcement Learning
This method is based on trial and error. The algorithm learns by interacting with a setting and receiving rewards or consequences. Self-driving carriages and game-playing AI (like AlphaGo) rely heavily on reinforcement learning.
Key Algorithms in Supervised Learning
Let’s break down some shared supervised learning algorithms in humble terms.
Linear Regression
This is like sketching a conventional line through data points to forecast outcomes. It’s often secondhand in forecasting numerical values, such as sales predictions.
Logistic Regression
Despite the name, it’s used for classification, not regression. For example, predicting whether an email is spam or not.
Decision Trees
These algorithms make decisions like a flowchart. Each “branch” represents a choice, leading to an outcome. They’re easy to understand and interpret.
Random Forest
A collection of decision trees combined. Instead of relying on one tree, it aggregates multiple trees to improve accuracy and avoid errors.
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
SVM tries to find the best boundary (or line) that separates different classes. Imagine drawing a line on paper that best divides two groups of dots.
k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)
This algorithm looks at the closest data points to make predictions. For instance, if most of your neighbors own a certain type of car, k-NN might predict you’ll own one too.
Key Algorithms in Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning focuses on discovering patterns when the answers aren’t given.
K-means Clustering
It groups data points into clusters based on similarity. E-commerce platforms use it to segment customers into groups for targeted marketing.
Hierarchical Clustering
This creates a tree-like structure of clusters, often used for organizing documents or genetic research.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
PCA reduces the complexity of data while preserving its important features. It’s commonly used for simplifying datasets in image recognition or medical diagnostics.
Reinforcement Learning Algorithms
Reinforcement learning focuses on learning from actions.
Q-learning
A model-free algorithm that helps an agent decide the best action to take based on rewards. For example, a robot learning to walk by trial and error.
Deep Q Networks (DQN)
An advanced version of Q-learning that combines deep learning with reinforcement learning. It’s widely used in game AI and robotics.
How Machine Learning Algorithms Work Step by Step
- Data Collection – Gather relevant data such as customer transactions, images, or sensor readings.
- Training the Model – Feed the data into the chosen algorithm so it can learn patterns.
- Making Predictions – The trained model applies what it learned to new, unseen data.
- Evaluating Results – Metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall are used to check performance.
Real-Life Examples of Machine Learning Algorithms
- Email Spam Detection: Logistic regression and decision trees are used to filter out junk emails.
- E-commerce Recommendations: K-means clustering and collaborative filtering help suggest products you might like.
- Self-Driving Cars: Reinforcement learning algorithms allow cars to “learn” safe driving practices.
Machine Learning in E-commerce and Marketing
Machine learning has transformed e-commerce email marketing and customer engagement. By using algorithms like clustering, businesses can segment users and personalize recommendations. For marketing and email campaigns, predictive models help target the right audience at the right time, improving ROI.

Challenges in Understanding Machine Learning
While machine learning algorithms are powerful, they can feel overwhelming. Terms like “support vector machines” or “deep Q networks” may sound complex, but at their core, they’re all about recognizing patterns. The real challenge lies in ensuring the data is clean, unbiased, and large enough to train models effectively.
Why Simplicity Matters in Learning Machine Learning
Explaining algorithms in simple language helps both beginners and professionals. Just like teaching a concept with stories and analogies, simplifying machine learning ensures more people can understand and apply it, not just data scientists.
Conclusion
Machine learning algorithms may sound intimidating, but when explained simply, they’re not much different from how humans learn. Whether it’s supervised learning like predicting house prices, unsupervised clustering for customer groups, or reinforcement learning in self-driving cars, these algorithms power modern technology. Understanding them opens doors to endless opportunities in business, marketing, and innovation.
Q1: What is the simplest machine learning algorithm to understand?
Linear regression is often the easiest because it’s just about drawing a straight line to predict values.
Q2: How are supervised and unsupervised learning different?
Supervised learning uses labeled data, while unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data.
Q3: Is machine learning the same as AI?
Machine learning is a subset of AI. AI is the broader field, while machine learning focuses on learning from data.
Q4: What algorithms are used in e-commerce?
Clustering, recommendation systems, and regression algorithms are commonly used in e-commerce for customer targeting.
Q5: Do I need coding to learn machine learning?
Basic coding skills in Python or R are helpful, but many platforms now offer user-friendly tools to start without heavy coding.

