Starting a career in data science is one of the most thrilling choices you can make today. Every manufacturing, from healthcare to economics, is looking for people who can turn raw data into clear insights. If you have ever wondered how to become a data scientist or how to get into data science, this guide will walk you through all you need. Think of it as a data science step-by-step trail that will help you study the basics, travel different courses, and comprehend how to grow into this demanding career.
Data Science 101: Understanding the Basics
The first stage to becoming a data scientist is knowing the basics. Many people call this phase data science 101 because it covers the basics of the field. You will need to know what data science is and why it is essential. At its core, data science is about gathering, cleaning, examining, and understanding large sets of data.
A data scientist uses figures, programming, and problem-solving to help trades make decisions. If you are just starting with data science, it is good to begin with ideas like types of data, humble data analysis, and the basics of algorithms.
Learning Path and Data Scientist Curriculum
Once you comprehend the basics, the next stage is exploring the data scientist curriculum. This comprises subjects like statistics, machine learning, data visualization, and programming languages such as Python and R. Many academies offer an outline of a data science course, but you can also learn a data scientist through stages like Coursera, Udemy, or edX.
Online agendas allow you to study data science at your own pace and fit it into your agenda. For someone who wants to learn to be a data scientist rapidly, online courses are an applied option. They often include pointers on projects that involve real-world circumstances.
How to Learn Data Science Step by Step
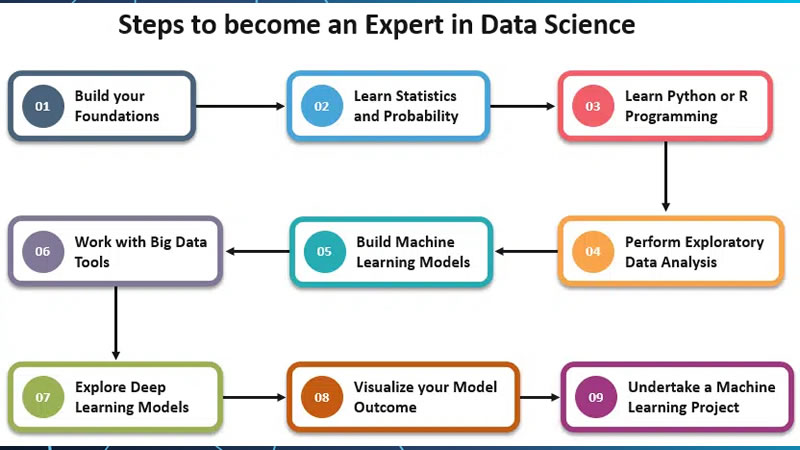
If you are asking yourself how I can become a data scientist, it is helpful to follow a clear step-by-step method. Here is one way to construct your knowledge:
Step 1: Master the basics. Focus on mathematics, statistics, and Python software design. These are the construction blocks of every data discipline scheme.
Step 2: Move into applied learning. Practice examining datasets, making visualizations, and building small machine learning models. This stage is around putting philosophy into action.
Step 3: Explore specialized fields. Data science is a comprehensive area, so you can dive more deeply into themes like natural language processing, deep learning, or commercial analytics contingent on your attention.
Step 4: Build a portfolio. Becoming a data scientist requires tools of skill. Upload schemes on GitHub or write about your knowledge expedition. Employers like to see how you share your knowledge.
Step 5: Keep learning. Data science knowledge never ends since the field keeps evolving. Reading investigation papers and following manufacturing news will help you stay efficient.
Becoming a Data Scientist for Beginners
For whole beginners, it can feel irresistible to study data science. The good news is that you do not need to be a skilled right absent. Becoming a data scientist is like learning a new language. At first, you emphasize vocabulary, then simple verbs, and over time, you become fluent. If you want a mild start, books like Data Science for Learners or connected bootcamps with guided education are helpful. These resources explain multifaceted ideas in simple terms so you can build confidence step by step.
Learn Data Science Online and Practice Daily
In today’s world, you do not have to join a full-time university database to become a data expert. Many professionals learn data expertise online and still land robust jobs, full Time Freelance. The key is constancy. Dedicate a small quantity of time each day to data science learning. Even thirty minutes consumed solving glitches, reviewing code, or travelling to a new dataset will add up to the end time. Remember, the trip of learning data science is not about whoosh but about building strong ways.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Data Scientist
One common query is how long it takes to develop a data scientist. The answer is contingent on your context and how much time you can give. If you previously know some programming and mathematics, you may be able to study to be a data scientist in fewer than a year through absorbed study. If you are starting from scratch, it may take longer. The significant part is not the speed but the steady development. Employers value skills, projects, and problem-solving more than the exact distance of your learning path.
Study Data Science with Real Projects
Theory alone is not sufficient. To truthfully become a data scientist, you must repeat with real data. Many free datasets are obtainable online. Try examining sales data, sports statistics, or even social media tendencies. Working on plans helps you connect your knowledge with practical consequences. For example, forecasting house prices using reversion models or building a simple reference system will show you how the ideas work in the real world. These schemes also become valued parts of your assortment when you apply for occupations.
Data Scientist Basics for Career Growth
As you move onward, do not forget the fundamentals. Skills like clear communication, problem-solving, and business savvy are just as significant as technical knowledge. A data scientist who can explain consequences in simple language will always stand out. If you keep asking how to be a data scientist who enhances value, the answer is to blend practical skills with real-world requests.
Starting a vocation in data science may seem like a huge test, but by breaking it down into steps, it becomes much calmer. Begin with data science 101, follow the data scientist curriculum, and practice frequently with schemes. Whether you learn data science online or through an official overview of a data science course, the key is consistency.
Anyone can develop into a data scientist if they are willing to learn, repeat, and grow. Your journey may seem small, but with endurance and effort, you will find yourself moving from a novice to a self-assured professional ready to take on real data tests.

