Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a concept reserved for sci-fi movies or high-tech labs. It has become an integral part of our daily lives, from the recommendations we receive on streaming platforms to the smart assistants in our homes. If you are new to the world of AI, understanding what it is and how it works can seem overwhelming. This beginner’s guide aims to simplify the topic, introduce you to AI basics, and give you a glimpse into the future of Artificial Intelligence.
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence, often abbreviated as AI, is the branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that would normally require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and even making decisions.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence begins with recognizing that AI is not a single technology but a combination of various tools and approaches. At its core, AI involves programming machines to mimic human cognitive functions. While humans rely on experience and intuition, AI systems rely on algorithms, data, and patterns to “learn” and make informed decisions.

For beginners, one of the most helpful ways to understand AI is to think of it in terms of applications you encounter every day. For instance, when you use Google Maps to find the fastest route home, AI algorithms analyze traffic patterns and suggest the most efficient path. Similarly, when Netflix recommends a show you might enjoy, it’s AI analyzing your past viewing habits and comparing them with similar users.
AI Basics Explained
Before diving deeper, it is important to cover some AI basics explained in a way that beginners can easily grasp. AI can be broadly classified into two categories: Narrow AI and General AI.
Narrow AI: Also called Weak AI, this type of AI is designed to perform a specific task. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, spam email filters, and recommendation systems. Narrow AI operates under predefined constraints and cannot perform tasks beyond its scope.
General AI: Also known as Strong AI, this type of AI aims to replicate human intelligence across a wide range of tasks. Unlike Narrow AI, General AI would have the ability to reason, solve unfamiliar problems, and learn in ways similar to humans. While General AI remains largely theoretical, it represents the ultimate goal of AI research.
Another key concept in understanding Artificial Intelligence is Machine Learning (ML). Machine Learning is a subset of AI where machines learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following fixed rules, an ML system identifies patterns in data and makes predictions or decisions based on those patterns. For example, email services use machine learning to distinguish between spam and legitimate emails, improving their accuracy over time.
A related concept is Deep Learning, a subset of Machine Learning that mimics the human brain’s neural networks. Deep Learning has enabled significant advancements in AI, including image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving.
How AI Works
To truly understand Artificial Intelligence, it helps to explore how AI systems work. At a high level, AI involves three main components: data, algorithms, and computing power.
Data: AI relies on large datasets to “learn.” The quality and quantity of data directly impact an AI system’s performance. For example, a facial recognition system trained on diverse datasets can accurately identify faces across different demographics.
Algorithms: Algorithms are the instructions that AI systems follow to analyze data and make decisions. These can range from simple rule-based algorithms to complex neural networks.
Computing Power: Modern AI requires significant computing resources. Powerful processors and cloud computing enable AI systems to process vast amounts of data quickly, allowing for real-time decision-making in applications like autonomous vehicles or voice assistants.
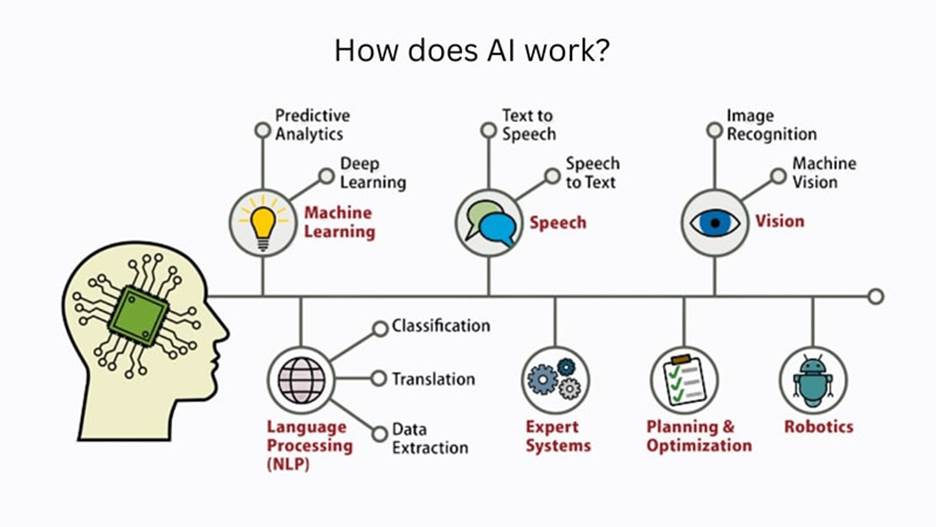
For beginners, it’s helpful to think of AI as a combination of three layers: perception, reasoning, and action. Perception involves gathering and interpreting data from the environment, reasoning involves analyzing that data to make decisions, and action involves executing the decisions.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI is no longer limited to laboratories; it is transforming industries across the globe. Some of the most prominent applications include:
Healthcare: AI algorithms can analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and assist in drug discovery. AI-driven chatbots also provide initial consultations and health guidance.
Finance: AI helps detect fraudulent transactions, optimize investment strategies, and personalize banking services for customers.
Education: AI-powered tools provide personalized learning experiences, automate grading, and analyze student performance to improve teaching methods.
Transportation: Self-driving cars and traffic management systems rely heavily on AI for navigation, safety, and efficiency.
Entertainment: AI recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube enhance user experience by predicting what content users are most likely to enjoy.
Customer Service: Virtual assistants and chatbots handle routine customer queries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Benefits and Challenges of AI
Understanding Artificial Intelligence also involves recognizing its benefits and challenges.
Benefits:
Efficiency and Productivity: AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on creative and strategic work.
Accuracy and Precision: AI systems reduce errors in tasks like medical diagnostics, data analysis, and quality control.
Decision-Making Support: AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, providing insights that help humans make better decisions.
Innovation: AI drives innovation across industries, leading to new products, services, and business models.
Challenges:
Ethical Concerns: Issues like data privacy, bias in algorithms, and autonomous decision-making raise ethical questions.
Job Displacement: Automation can lead to job loss in certain sectors, although it also creates new opportunities in AI development and maintenance.
Complexity: Developing and maintaining AI systems requires specialized knowledge and significant resources.
Security Risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to attacks, such as adversarial inputs designed to deceive machine learning models.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of Artificial Intelligence holds immense potential and exciting possibilities. Experts predict that AI will become more integrated into our daily lives, enhancing everything from healthcare and education to transportation and entertainment.

Some trends shaping the future of AI include:
Explainable AI (XAI): Future AI systems will be designed to provide transparent explanations for their decisions, making them more trustworthy and easier to regulate.
AI in Creativity: AI will increasingly assist in creative tasks, such as composing music, generating artwork, and writing content, opening new avenues for human-AI collaboration.
Autonomous Systems: Self-driving vehicles, drones, and robotic assistants will become more common, transforming industries like logistics, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Personalized Experiences: AI will continue to improve personalization in areas like education, entertainment, healthcare, and retail, tailoring experiences to individual needs and preferences.
AI Ethics and Governance: As AI becomes more pervasive, governments and organizations will establish regulations to ensure ethical use, prevent bias, and protect privacy.
For beginners, it’s exciting to note that AI is still in a stage of rapid evolution. Learning the fundamentals now provides a strong foundation for understanding how AI will shape our future.
Getting Started with AI for Beginners
If you’re intrigued by AI and want to explore it further, there are several steps you can take to get started:
Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with AI concepts, terminology, and applications. Free online courses, tutorials, and beginner-friendly books are great resources.
Understand Machine Learning: Since Machine Learning is a core component of AI, learning the basics of ML algorithms and their applications is essential.
Experiment with Tools: Platforms like Google Colab, TensorFlow, and PyTorch allow beginners to experiment with AI projects without advanced setup.
Follow AI News and Trends: Staying updated on AI developments helps you understand its practical applications and potential future directions.
Build Projects: Hands-on experience is crucial. Start with small projects like chatbots, image classifiers, or recommendation systems to reinforce your learning.

Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a transformative technology that is reshaping industries, enhancing human capabilities, and redefining the way we interact with machines. For beginners, understanding AI basics explained in simple terms provides a strong foundation to explore its vast potential. From everyday applications like voice assistants and recommendation systems to groundbreaking innovations in healthcare and autonomous vehicles, AI is becoming an essential part of modern life.
By learning the fundamentals of AI, understanding its applications, and staying informed about emerging trends, you can position yourself to participate in the exciting future of Artificial Intelligence. Whether your interest lies in programming, ethical considerations, or simply understanding how AI impacts daily life, this beginner’s guide provides a roadmap to navigate the fascinating world of AI.
1. What is Artificial Intelligence in simple terms?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and make decisions. It allows computers to perform tasks like problem-solving, language understanding, and pattern recognition.
2. How does AI work?
AI works by analyzing large amounts of data using algorithms. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, enables systems to learn from this data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
3. What are the different types of AI?
There are two main types: Narrow AI, which performs specific tasks like virtual assistants, and General AI, which aims to replicate human-level intelligence across various tasks.
4. Why is AI important for beginners to learn?
Learning AI basics gives beginners insight into how technology is shaping industries, enhances problem-solving skills, and prepares them for future opportunities in careers involving AI, data science, and automation.
5. What is the future of Artificial Intelligence?
The future of AI includes more advanced autonomous systems, personalized experiences, ethical AI governance, and creative applications. AI will continue to impact healthcare, education, transportation, and many other areas, making it a crucial technology for the coming decades.

